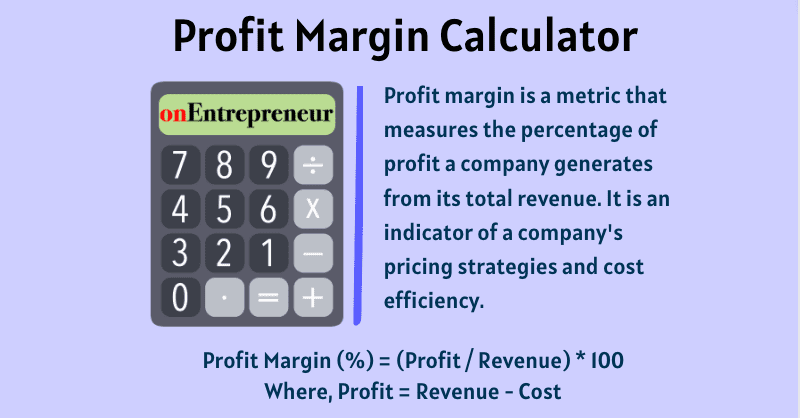
Enter your parameters in the profit margin calculator below:
How to use this Profit Margin Calculator?
- Enter the value of cost and the desired profit margin.
- Press CALCULATE to calculate the value of revenue and profit based on the entered cost and desired profit margin value.
- Click RESET to reset the entered values and start a new calculation. (You can also start a new calculation without pressing RESET).
What is Profit Margin?
Profit margin is a metric that measures the percentage of profit a company generates from its total revenue. It is an indicator of a company’s pricing strategies and cost efficiency.
The formula for profit margin is:
Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100
For example, if a company has $1 million in revenue and $250,000 in net profit, its profit margin is:
($250,000 / $1,000,000) x 100 = 25%
(You can validate this result by entering the values of Cost and Profit Margin as $750000 and 25% respectively in the above profit margin calculator)
A higher profit margin indicates that a company is more efficiently generating profits from its revenues. However, an extremely high profit margin may indicate the company is overpricing its products. A low profit margin may signal inefficient operations or aggressive pricing strategies to gain market share.
Key things to know about profit margin:
- Expressed as a percentage of revenue
- Measures profitability from core operations
- Used to compare companies in the same industry
- An increase over time generally indicates improved efficiency
- Different industries have varied acceptable profit margins
- Doesn’t account for total company value or asset costs
Profit margin is a helpful metric for investors to gauge the operational efficiency and pricing power of a company over time. Comparing profit margins between competitors illustrates differences in business models and strategies. Overall, a healthy and consistent profit margin reflects sound financial management.
Profit Margin Formula and Example
For example, a 20% profit margin means there is $20 of net income for every $100 of revenue. The formula to calculate profit margin is:
Where, (Revenue – Cost) = Profit
The profit margin represents the percentage of profit in the total revenue. For example, you sell an item for $10 with a cost of $8. Here, your profit is $10 – $8 = $2. So, the profit margin is ($2/$10)*100 = 20%.
In the above pie chart, the full circle represents the total revenue. The red portion shows the part of the cost in revenue while the blue portion shows the part of the profit which is the profit margin. So, the profit margin simply tells the percentage of profit in revenue.
In the above example, if you sell the item at $12, then your profit is $4 and the profit margin is ($4/$12)*100 = 33.33%, which is one-third of the revenue. An increase in profit increases the profit margin.
Different types of profit margins with formula
Here are 6 common types of profit margins and their formulas:
1. Gross profit margin:
Measures profit after accounting for the costs of goods sold.
Formula: (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue
2. Operating profit margin:
Calculates profit after operating expenses are deducted.
Formula: (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold – Operating Expenses) / Revenue
3. Net profit margin:
The ratio of net income to total revenue. Shows the percentage of revenue retained as profit after all expenses.
Formula: Net Income / Revenue
4. EBITDA margin:
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization divided by total revenue. Helps compare profitability across companies.
Formula: (Net Income + Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization) / Revenue
5. Return on assets (ROA):
Measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate profit.
Formula: Net Income / Total Assets
6. Return on equity (ROE):
Calculates a firm’s efficiency at generating profits from shareholders’ equity.
Formula: Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
Tracking these key profitability ratios over time can provide insight into the financial health and performance of a business. Comparing margins to industry benchmarks is also useful for assessing the company’s position.
What is a good profit margin?
There is no single “good” profit margin that applies to all businesses. However, here are some general guidelines for profit margins:
- Retail businesses: Aim for a gross profit margin of at least 30-40%. Net profit margins tend to be lower, around 5-10%.
- Manufacturers: Gross margins are often around 40-50%. Net margins vary more widely based on the industry, but 10-20% is common.
- Software/SaaS: Gross margins are typically 70-80% due to low variable costs. Net margins can range from 15-50%+.
- Professional services: Gross margins are commonly 50-60%. Net margins are often 15-25%.
- Restaurants: Gross margins are around 60-70%. However, net margins are only around 3-6% due to high fixed costs.
The optimal margin depends on your industry, business model, strategy, and stage of business. When evaluating your profit margin, compare it to industry benchmarks and track it over time to ensure it aligns with your business goals. A low margin may indicate problems with pricing, costs or efficiency. An extremely high margin could mean missing growth opportunities.
Why is profit margin important?
Profit margin is one of the commonly used profitability ratios to assess your profit. It is one of the financial metrics used to evaluate a company’s ability to generate earnings in relation to its revenue. To stay fiscally healthy, businesses must pay attention to profit margins. Profit margins indicate how well a company is performing. A high value of profit margin indicates that a company can control its costs in an effective way through efficient management.
Why Profit Margin is always less than 100%?
The profit margin is 100% when revenue is equal to the profit. That means you are selling something that costs zero to generate revenue. This is an absurd case and only possible when you are selling items you got for free like donations and gifts.