In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven business landscape, organizations across industries are constantly seeking ways to optimize their operations, improve productivity, and gain a competitive edge. One solution that has gained significant prominence is the implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. By integrating and streamlining various business processes, ERP systems enable organizations to effectively manage their resources, make informed decisions, and enhance overall efficiency.
According to research, an ERP system can help an organization grow and sustain its business. Moreover, the latest statistics show that the revenue in the Enterprise Resource Planning Software market is estimated to reach US$49.38 billion in 2023, with a projected annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2028) of 4.78%, leading to a market volume of US$62.36 billion by 2028.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of ERP systems and different modules, explore their functionalities, and benefits, and discuss how they have revolutionized modern business management.
Defining Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to the integrated management of an organization’s core business processes through the use of software and technology. Typically, an ERP system consists of a suite of interconnected applications that enable the collection, storage, management, and interpretation of data from diverse business activities.
By utilizing a common database maintained by a database management system, ERP systems provide a real-time, holistic view of an organization’s operations, facilitating seamless information flow and data sharing across departments.
Some typical Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) modules
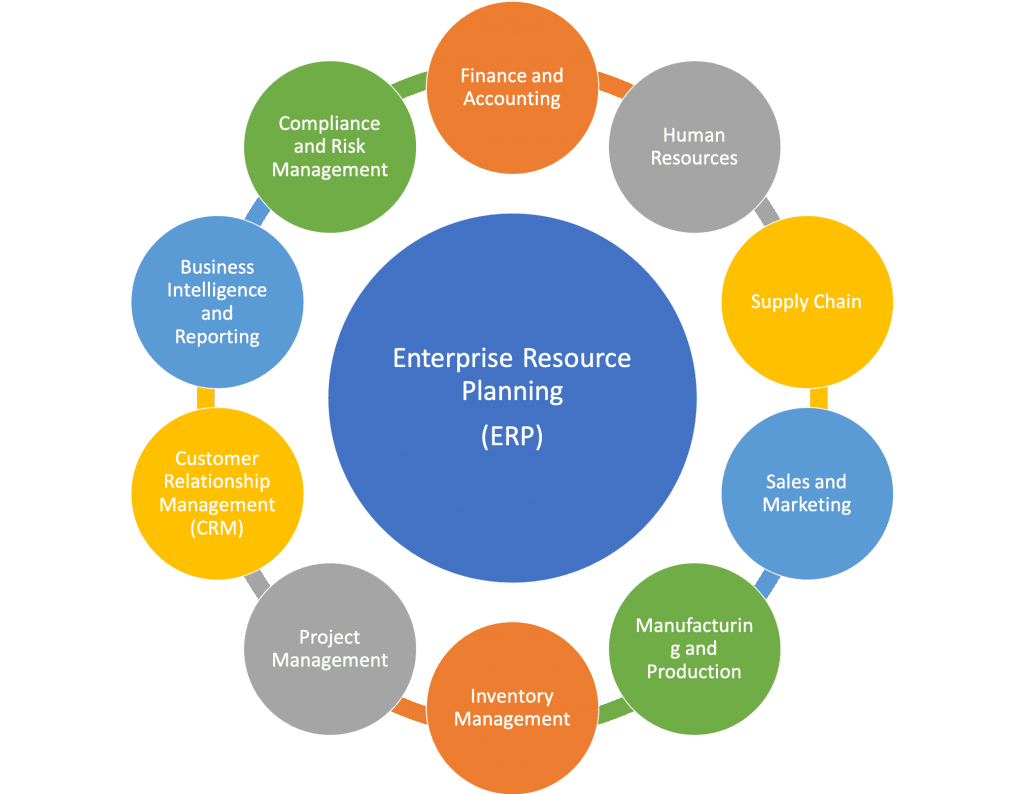
1. Finance and Accounting Module
The finance and accounting module in an ERP system handles financial transactions, general ledger management, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. It provides organizations with a comprehensive view of their financial health, enabling effective financial planning and decision-making.
2. Human Resources Module
The human resources module focuses on managing employee-related information, such as employee profiles, attendance, payroll, benefits administration, performance evaluations, and training records. This module streamlines HR processes, enhances workforce management, and ensures compliance with labor laws and regulations.
3. Supply Chain Management Module
The supply chain management module encompasses activities related to procurement, inventory management, order processing, logistics, and supplier relationship management. It enables organizations to optimize their supply chain operations, minimize costs, manage inventory efficiently, and enhance customer satisfaction through timely order fulfillment.
4. Sales and Marketing Module
The sales and marketing module helps organizations manage their sales processes, customer relationship management (CRM), lead generation, sales forecasting, and marketing campaigns. It provides sales teams with real-time access to customer information, improves customer engagement, and enables targeted marketing strategies.
5. Manufacturing and Production Module
The manufacturing and production module focuses on managing the production processes, including material requirements planning (MRP), production scheduling, shop floor control, quality control, and product lifecycle management. It enables organizations to optimize production efficiency, minimize lead times, and ensure product quality and compliance.
6. Inventory Management Module
The inventory management module facilitates the tracking and management of inventory levels, stock movements, and stock valuation. It provides organizations with real-time visibility into inventory, helping them optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
7. Project Management Module
The project management module helps organizations plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively. It includes features such as project planning, resource allocation, task management, progress tracking, and collaboration tools. This module enables organizations to achieve project goals within the allocated time, budget, and resources.
8. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module
The CRM module focuses on managing customer interactions, sales opportunities, customer service, and support. It helps organizations nurture customer relationships, track customer interactions, and improve customer satisfaction and retention.
9. Business Intelligence and Reporting Module
The business intelligence and reporting module provides organizations with analytical tools and reporting capabilities to gain insights from their data. It enables data visualization, performance monitoring, and data-driven decision-making, helping organizations identify trends, make informed decisions, and drive business growth.
10. Compliance and Risk Management Module
The compliance and risk management module helps organizations adhere to regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies. It includes features for risk assessment, compliance monitoring, audit management, and incident tracking. This module ensures organizations operate in a compliant and risk-aware manner, minimizing legal and operational risks.
These modules, among others, can be customized and tailored to meet the specific needs of an organization, providing a comprehensive and integrated solution for managing various aspects of their business operations.
The Functionality of ERP Systems
1. Streamlined Business Processes
At the heart of ERP systems lies the ability to streamline business processes. By automating manual tasks, eliminating redundant activities, and integrating data from various functions, ERP systems enable organizations to operate more efficiently. For example, consider a manufacturing company that adopts an ERP system. The system can seamlessly connect different departments, such as procurement, production, inventory management, and sales, allowing for improved coordination and resource allocation.
This streamlined approach minimizes delays, reduces errors, and enhances overall productivity.
2. Comprehensive Data Management
ERP systems serve as centralized repositories for all relevant business data. These systems consolidate information from multiple sources and provide a single source of truth for decision-making. Additionally, with real-time access to accurate and up-to-date data, managers can make informed decisions promptly, identify trends, and respond to market dynamics effectively.
For instance, sales managers can leverage ERP-generated reports to analyze customer buying patterns, identify high-demand products, and adjust marketing strategies accordingly.
3. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for the smooth functioning of any organization. ERP systems facilitate seamless information sharing and collaboration among departments, both within and across organizational boundaries. For instance, when a customer places an order, the sales team can instantly update the ERP system, triggering notifications to the relevant departments such as production, inventory, and shipping.
This ensures everyone involved in the process has access to the latest information, thereby minimizing miscommunication and reducing delays.
Benefits of Implementing an ERP System
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
By automating manual tasks, reducing redundant activities, and streamlining processes, ERP systems significantly enhance organizational efficiency and productivity. With standardized workflows, organizations can optimize resource allocation, reduce lead times, and accelerate overall business operations.
This increased efficiency translates into cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and a competitive advantage in the market.
2. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Decision-Making
One of the primary advantages of ERP systems is their ability to provide accurate, real-time data across the organization. With a centralized database, organizations can eliminate data silos, improve data integrity, and minimize the risk of errors resulting from manual data entry.
Moreover, ERP systems offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing managers to generate insightful reports, perform data-driven analysis, and make informed decisions promptly.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
ERP systems are designed to accommodate the evolving needs of organizations. Whether a company experiences organic growth, expands its operations, or ventures into new markets, ERP systems can scale accordingly. Moreover, with the advent of cloud-based ERP solutions, organizations have the flexibility to access and manage their systems from anywhere, at any time, with an internet connection.
This mobility ensures seamless operations even for globally distributed teams and enables efficient collaboration across locations.
Example Case Study: XYZ Corporation’s Successful ERP Implementation
To illustrate the transformative power of ERP systems, let’s examine the case of XYZ Corporation, a medium-sized manufacturing company that recently implemented an ERP system.
Pre-implementation Phase
XYZ Corporation faced numerous challenges due to disjointed and inefficient processes. Information was scattered across different departments, leading to delays in order fulfillment, inventory discrepancies, and poor coordination. Recognizing the need for a comprehensive solution, the company decided to implement an ERP system.
Implementation Phase
During the implementation process, XYZ Corporation worked closely with a trusted ERP provider to configure the system according to their specific requirements. The ERP system integrated various modules, including supply chain management, production planning, inventory control, and finance. Additionally, the key employees underwent comprehensive training to ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
Post-implementation Phase
Post-implementation, XYZ Corporation experienced significant improvements in its operations. The ERP system facilitated real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling the company to optimize procurement and reduce carrying costs. Also, production planning became more efficient, reducing lead times and enhancing customer satisfaction. Moreover, the centralized database improved collaboration and information sharing, leading to better decision-making across departments.
Conclusion
In today’s digital era, where data is abundant and business processes are increasingly complex, organizations must adopt modern tools and technologies to stay ahead. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as a game-changer, enabling organizations to integrate, streamline, and manage their core business processes effectively. Also, from improved efficiency and productivity to enhanced data accuracy and decision-making, ERP systems offer a multitude of benefits that drive organizational success. As technology continues to evolve, organizations that embrace ERP systems are poised to gain a competitive edge in an ever-changing business landscape.