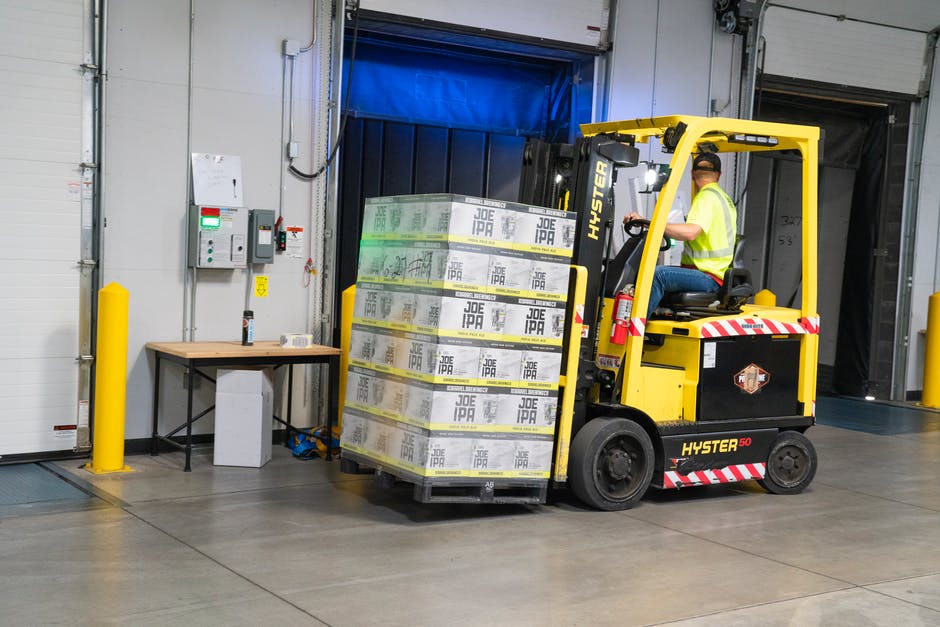
Companies are constantly seeking ways to optimize their supply chain operations. The global logistics market was valued at 8.4 trillion U.S. dollars in 2021 and is projected to surpass 13.7 trillion U.S. dollars by 2027. One approach that has gained significant traction is the utilization of third-party logistics providers, commonly known as 3PL.
To grasp the concept of a 3PL, we must first understand its core meaning. Third-party logistics (3PL) is a service offered by the logistics industry to enhance business performance and production for firms of all sizes. These specialized entities offer a range of services designed to streamline and enhance the logistics processes of businesses across various industries.
In this article, we will delve into the meaning of a 3PL, explore the key services they offer, and discuss the process of engaging with a 3PL partner.
3PL Meaning:
A third-party logistics provider is an external company that offers comprehensive logistics services to organizations. Unlike traditional logistics models where businesses handle their entire supply chain in-house, partnering with a 3PL allows companies to outsource specific functions or the entire logistics process. 3PLs act as intermediaries between manufacturers or suppliers and end customers, seamlessly integrating into the supply chain ecosystem.
Advantages of Partnering with a 3PL:
a) Expertise and Specialization:
One of the key advantages of engaging a 3PL is access to their specialized knowledge and expertise in managing complex logistics operations. These providers possess an in-depth understanding of industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements, enabling them to optimize supply chain activities more efficiently.
b) Cost Efficiency:
By outsourcing logistics functions to a 3PL, companies can benefit from significant cost savings. 3PLs leverage economies of scale, bulk purchasing power, and optimized transportation networks to negotiate favorable rates with carriers and suppliers. Moreover, businesses can avoid upfront investments in warehousing infrastructure, transportation assets, and technology, allowing them to allocate resources more effectively.
c) Scalability and Flexibility:
3PLs offer the scalability and flexibility necessary to accommodate varying business needs. As companies experience fluctuations in demand or expand into new markets, 3PLs can quickly adapt their operations to match these changes. They provide access to a vast network of distribution centers, transportation modes, and value-added services, ensuring seamless scalability without compromising on service quality.
d) Focus on Core Competencies:
Partnering with a 3PL allows businesses to concentrate on their core competencies. By entrusting logistics operations to a specialized provider, companies can redirect their internal resources toward activities that drive growth, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Key Services Offered by 3PL:
a) Transportation Management:
One of the fundamental services provided by 3PLs is transportation management. This involves planning, coordinating, and executing the movement of goods from one location to another. 3PLs leverage their extensive network of carriers to optimize freight routing, select the most cost-effective transportation modes, and ensure timely delivery.
b) Warehousing and Distribution:
3PLs operate advanced warehousing facilities strategically located to facilitate efficient inventory management and order fulfillment. These providers utilize sophisticated inventory tracking systems, employing best practices such as cross-docking, pick-and-pack, and just-in-time inventory management. Additionally, they offer value-added services like kitting, labeling, and packaging customization to meet specific customer requirements.
c) Inventory Management:
Effective inventory management is critical for optimizing supply chain performance. 3PLs employ advanced technologies and systems to track inventory levels, monitor stock movements, and ensure accurate demand forecasting. By streamlining inventory management processes, businesses can minimize stockouts, reduce carrying costs, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
d) Reverse Logistics:
3PLs also play a crucial role in managing reverse logistics, which involves handling product returns, repairs, and recycling. These providers have established processes and systems in place to handle reverse logistics efficiently, enabling businesses to recover value from returned products, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction.
The Process of Engaging with a 3PL:
a) Assessment and Evaluation:
When considering a partnership with a 3PL, companies should conduct a thorough assessment of their logistics requirements and align them with the capabilities of potential 3PL providers. Factors to consider include industry expertise, service offerings, technology infrastructure, geographical coverage, and scalability.
b) Request for Proposal (RFP):
After shortlisting potential 3PL partners, companies typically issue an RFP to gather detailed information about the providers’ capabilities, pricing models, service level agreements (SLAs), and key performance indicators (KPIs). This helps businesses compare and evaluate different proposals objectively.
c) Due Diligence and Selection:
The due diligence process involves analyzing the RFP responses, conducting site visits, checking references, and evaluating the financial stability and operational track record of potential 3PL partners. This rigorous assessment ensures that businesses select a reliable and trustworthy 3PL provider.
d) Contract Negotiation:
Once the preferred 3PL partner is identified, companies engage in contract negotiation to establish the terms and conditions of the partnership. This includes defining service levels, pricing structures, performance guarantees, data security protocols, and termination clauses. Engaging legal counsel during this stage is advisable to protect the interests of both parties.
e) Implementation and Collaboration:
The successful onboarding of a 3PL requires effective collaboration and communication between the company and the provider. This includes sharing relevant data and information, aligning IT systems, establishing key performance metrics, and conducting regular reviews to monitor performance and address any issues proactively.
Conclusion:
In an increasingly interconnected and fast-paced business environment, leveraging the expertise and resources of a 3PL can be a game-changer for companies striving to enhance their logistics operations. By partnering with a reliable 3PL provider, businesses can optimize their supply chain, improve customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. Understanding the definition of a 3PL, recognizing the advantages they offer, and following a systematic process for engagement can set the stage for a fruitful and mutually beneficial partnership between companies and their chosen 3PL providers.